The Role of Reverse Engineering in Mechanical Engineering
The Role of Reverse Engineering in Mechanical Engineering
What is Mechanical Engineering?
One of the most diverse and versatile engineering fields, mechanical engineering is the study of objects and systems in motion. As such, the field of mechanical engineering touches virtually every aspect of modern life.
The role of a mechanical engineer is to take a product from an idea to the marketplace. To accomplish this, the mechanical engineer must be able to determine the forces and thermal environment that a product, its parts, or its subsystems will encounter; design them for functionality, aesthetics, and durability; and determine the best manufacturing approach that will ensure operation without failure.
Mechanical engineers play key roles in a wide range of industries including automotive, aerospace, biotechnology, computers, electronics, microelectromechanical systems, energy conversion, robotics and automation, and manufacturing. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) currently lists 36 technical divisions, from advanced energy systems and aerospace engineering to solid-waste engineering and textile engineering.
Technically, mechanical engineering is the application of the principles and problem-solving techniques of engineering from design to manufacturing to the marketplace for any object. Mechanical engineers analyze their work using the principles of motion, energy, and force—ensuring that designs function safely, efficiently, and reliably, all at a competitive cost.
Reverse Engineering in Mechanical Engineering:
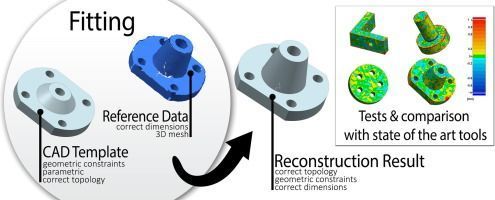
In mechanical engineering, the term reverse engineering (often abbreviated to RE) is used to summarize the process of reconstructing an existing object. When designing an object from scratch, an engineer will draw up a design specification and produce drawings from which the item is constructed.
Conversely, with reverse engineering, the design engineer starts with the final product and works through the design process in the opposite direction to arrive at the product design specification. During the process, vital information about the design concept and manufacturing methods is discovered.
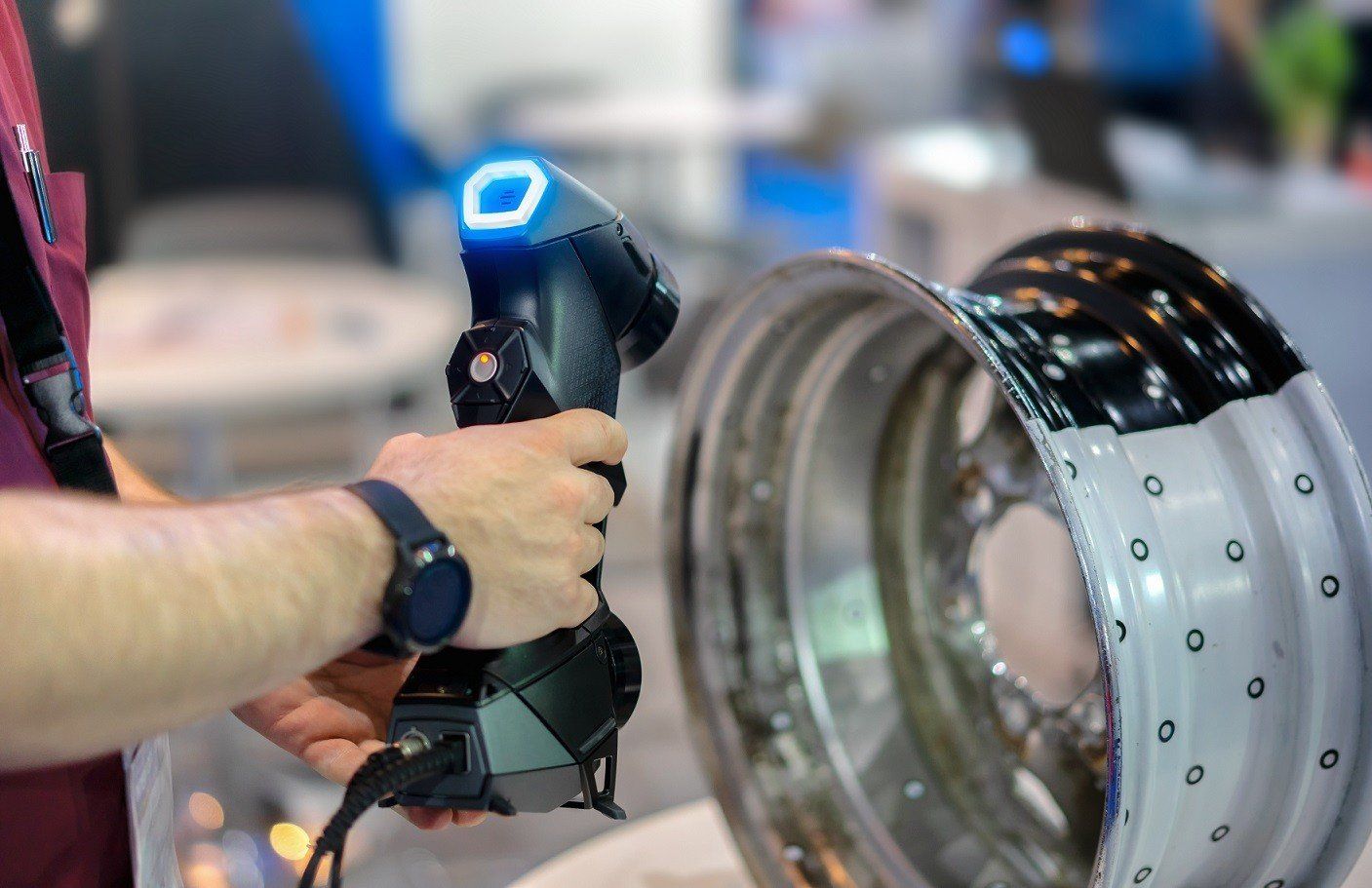
The process of RE begins by gaining dimensional information of the object via 3D scanning, whether it is a mechanical component, a consumer product or an ancient artefact.
Reverse engineering involves acquiring three-dimensional positional data in the point cloud. There are many ways of gathering valuable dimensional information about the product, but using an accurate 3D measuring system is paramount. The accuracy of the data captured will impact the quality and deviation of the Reverse Engineered model when compared to the original.
Physical Digital uses the globally-recognised GOM 3D structured light scanning systems, which offer highly-accurate, traceable and repeatable measurement. The surface data captured is then passed to our in-house design team to establish the original design intent of the object.
How is Reverse Engineering used in Mechanical Engineering?
RE enables the duplication of an existing part by capturing the component’s physical dimensions, features, and material properties. There are a wide range of reasons for reverse engineering an object, including:
Legacy Components – For many components that were designed and manufactured years ago, there are no existing 2D drawings or 3D CAD data from which to reproduce the object. Here, reverse engineering is a vital means to gain the information to recreate the product.
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) issues – If the OEM is no longer trading or has lost design measurements, then Reverse Engineering will supply the vital product information to continue manufacturing of that object.
Design Development, Part Testing & Analysis – Through reverse engineering, a 3D product can be quickly captured in digital form and remodelled or analysed in order to achieve improved design iterations.
Competitor Analysis – Any organisation can analyse competitor products through reverse engineering.
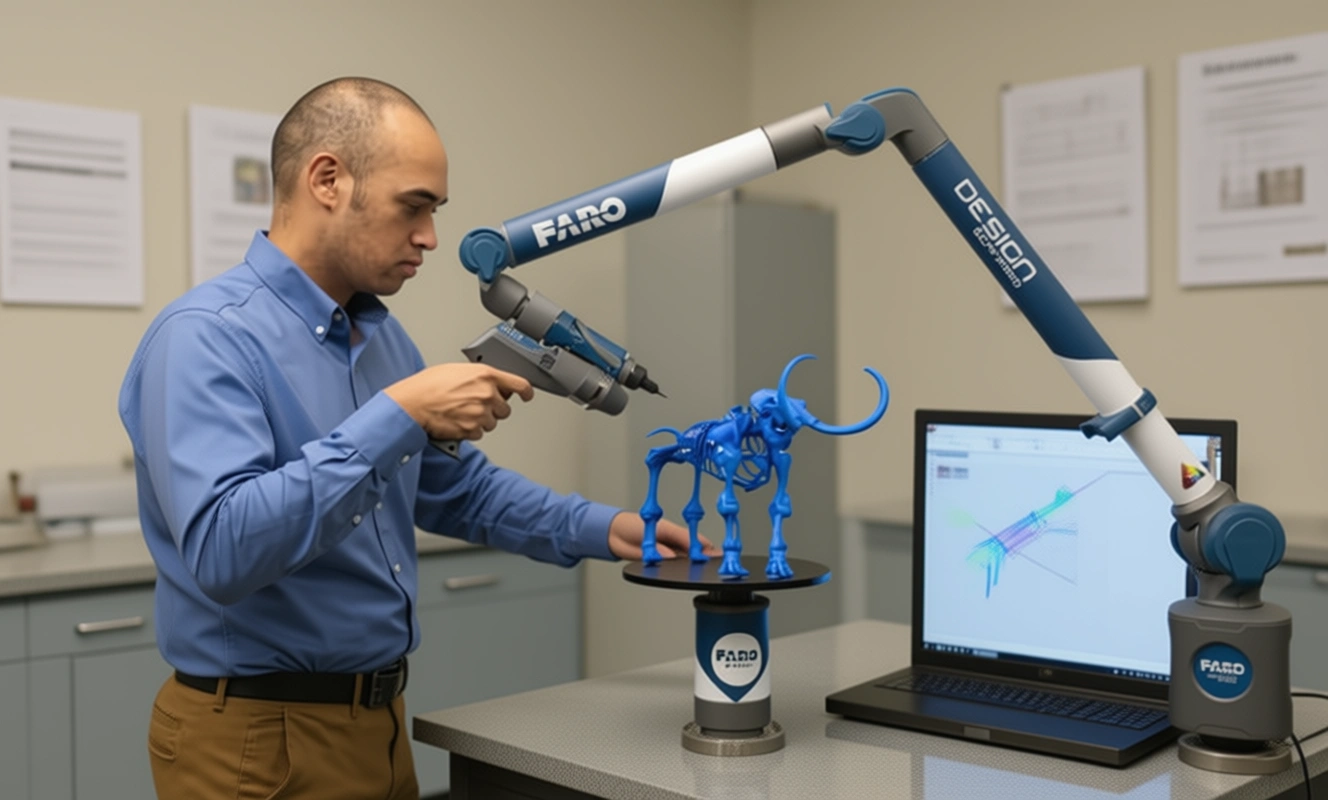
Bespoke and Ancient objects – Where there is no information about the dimensions of an object except for the physical item itself, the quickest and most reliable way to reproduce it will be by reverse engineering. Where a product is organic in shape (not a standard geometry such as cuboid or cylindrical), designing in CAD may be challenging as it can be difficult to ensure that the CAD model will be acceptably close to the sculpted model. Reverse engineering avoids this problem as the physical model is the source of the information for the CAD model.
Modern manufacturing – methods such as Additive Manufacturing rely on reverse engineering.
Digital Archiving – Museum pieces and historic artefacts can be captured through 3D scanning, then reverse engineered and the resulting CAD data can be held in case of any future damage to the object or any need to reproduce parts of the item.

If you want to explore more about Reverse Engineering, other CAD software and how to master them, check out our Blog Posts here or contact us here to get in touch with a Reverse Engineering expert!






There are no comments