Top 4 3D Scanning Techniques for Reverse Engineering
Top 5 3D Scanning Techniques for Reverse Engineering
3D scanning has revolutionized the field of reverse engineering, offering precise and efficient ways to capture physical objects digitally. Whether you’re involved in product design, quality control, or prototyping, understanding the various 3D scanning techniques can significantly enhance your projects. Here are the top five methods that stand out in the realm of reverse engineering.
1. Laser Scanning
Laser scanning is one of the most popular 3D scanning techniques. It uses laser beams to capture the surface geometry of an object with high accuracy. The data collected is then processed into a point cloud, which can be converted into a detailed 3D model.
- Pros: High precision and detail.
- Cons: Can be expensive and requires post-processing software.
2. Structured Light Scanning
This technique employs projected light patterns onto an object to capture its shape. By analyzing the deformation of these patterns, structured light scanners create a 3D representation of the object.
- Pros: Fast data acquisition and excellent for complex geometries.
- Cons: Less effective in bright environments.
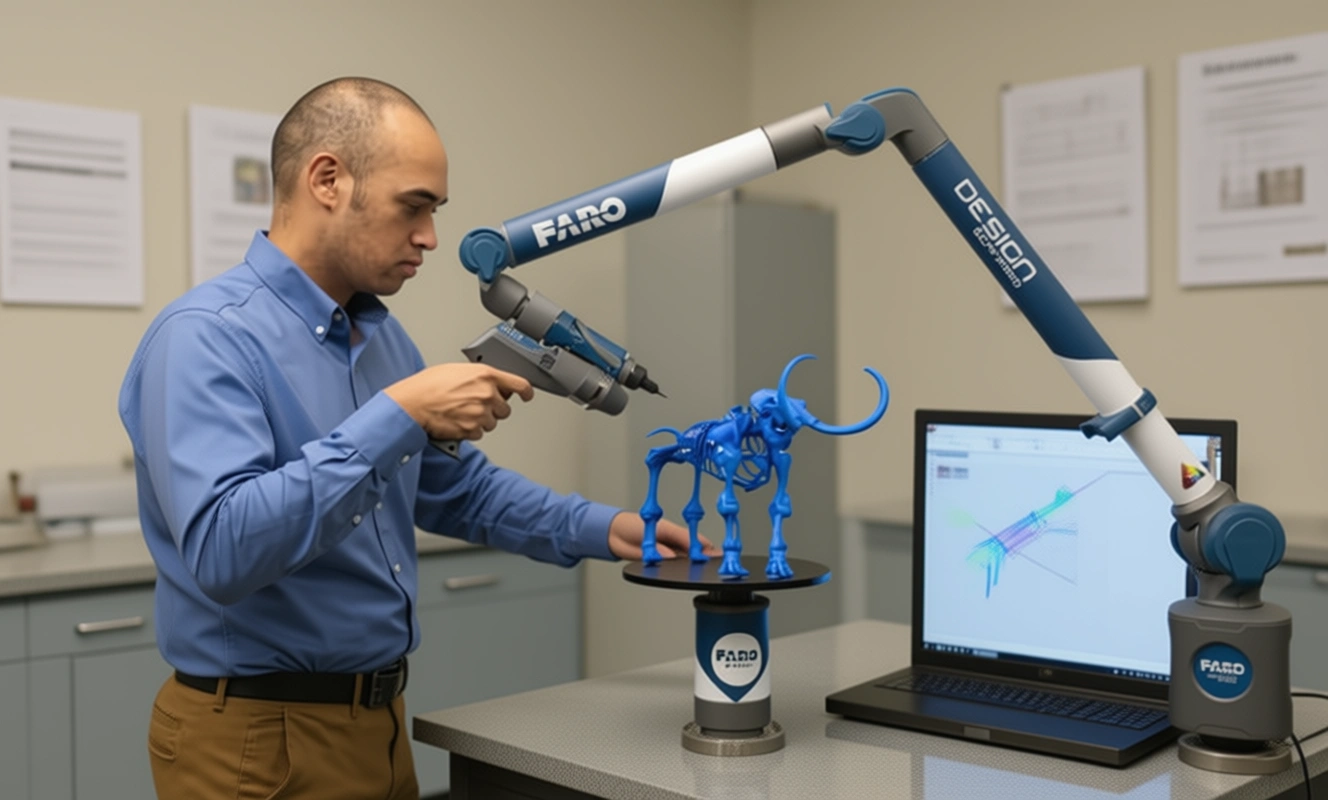
3. Contact Scanning
Contact scanning involves physically touching the object with a probe to collect data points. This method is particularly useful for capturing intricate details on small parts where precision is critical.
- Pros: Extremely accurate for small components.
- Cons: Time-consuming and not suitable for fragile objects.
4. Photogrammetry
This technique utilizes photographs taken from different angles to reconstruct a 3D model through software algorithms. It’s an accessible option as it often requires only a camera and specialized software.
- Pros: Cost-effective and versatile; great for large objects.
- Cons: Accuracy depends on image quality and lighting conditions.
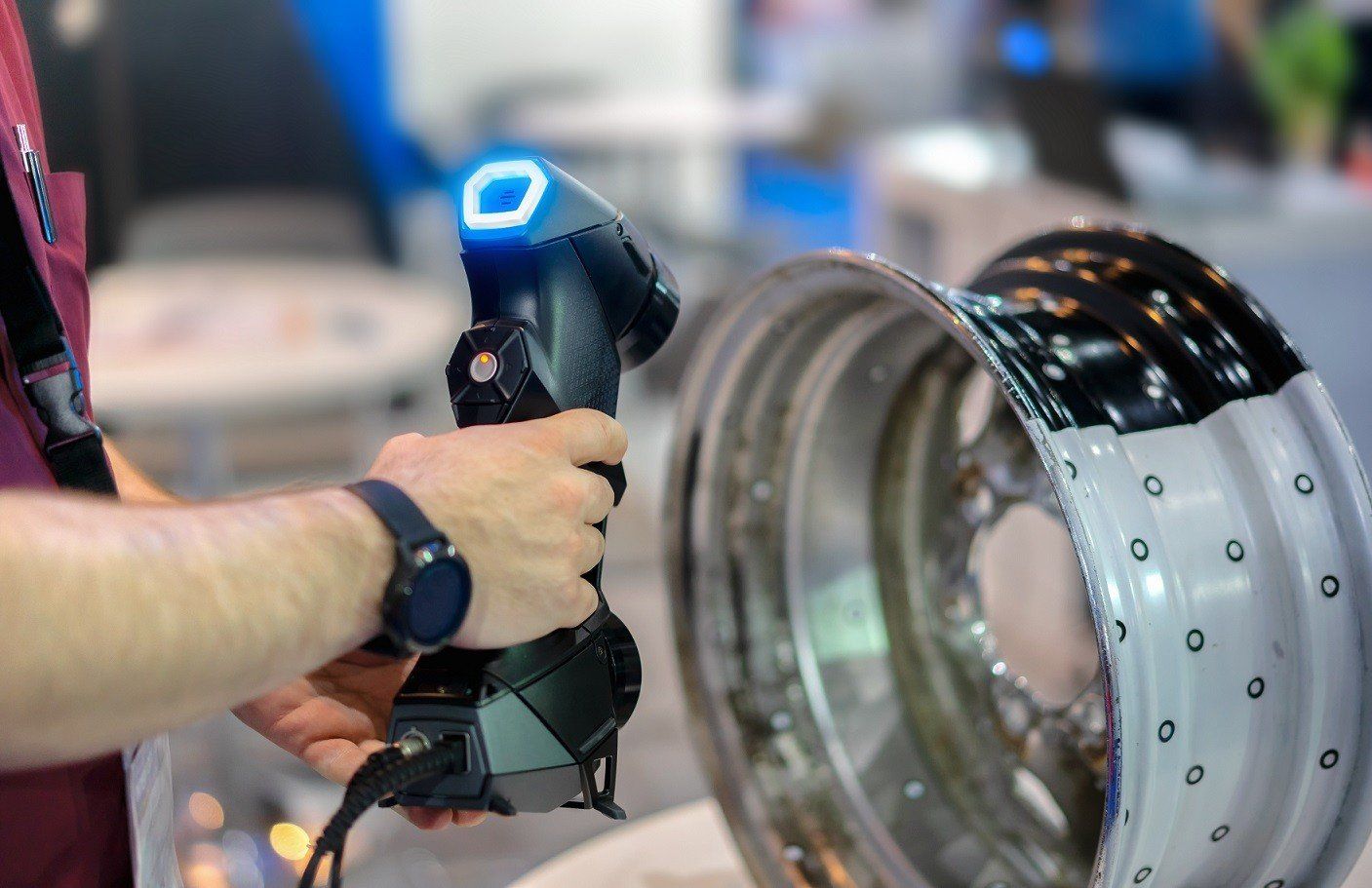
5. Handheld Scanning
Handheld scanning allows users to capture 3D data of an object by moving a portable scanner around it. This technique combines the flexibility of mobility with ease of use, making it suitable for various applications.
- Pros: Highly portable and user-friendly.
- Cons: May lack the precision of stationary methods.
How can we help you?
Do you have further questions about us or reverse engineering? Contact us anytime! We are looking forward to your message.
Would you like to learn more about exciting reverse engineering topics? Please visit us on YouTube! There we regularly provide videos on exciting topics.






There are no comments